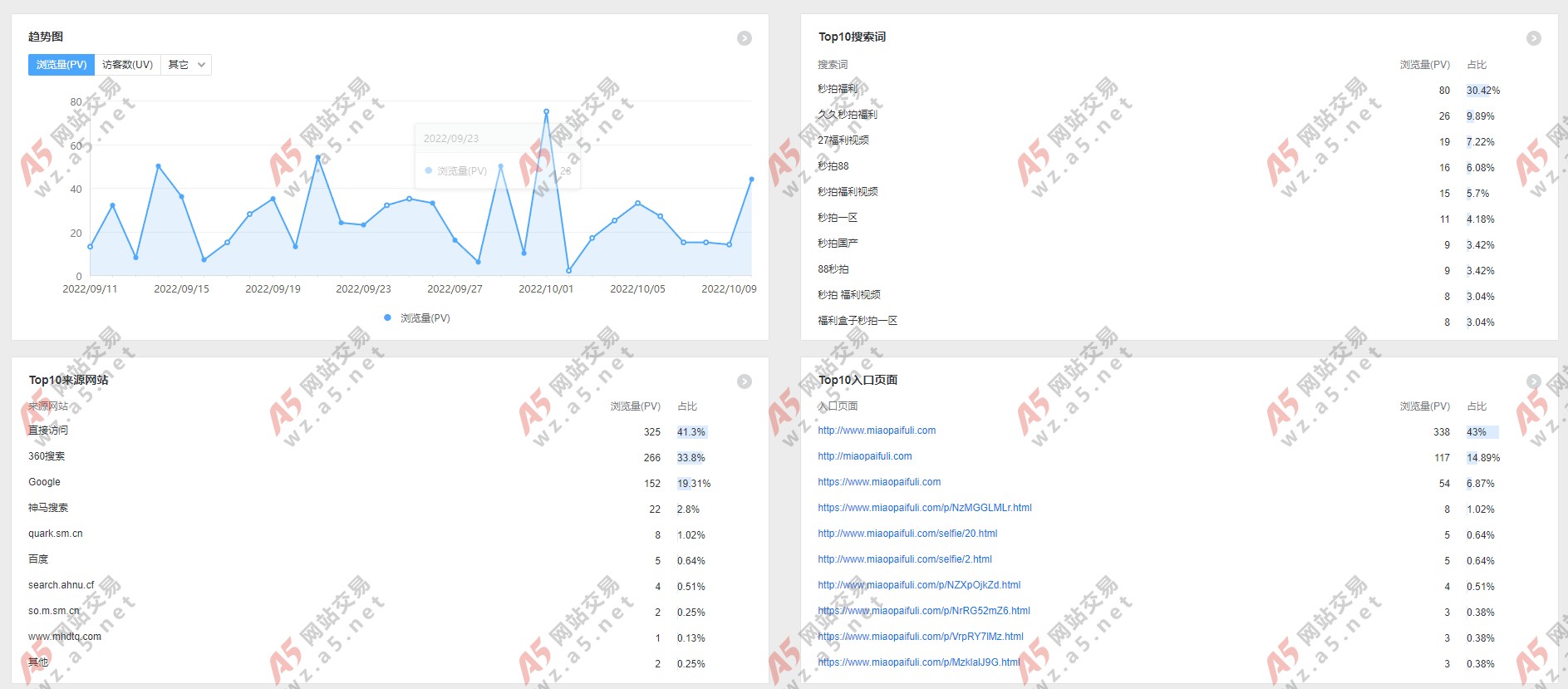
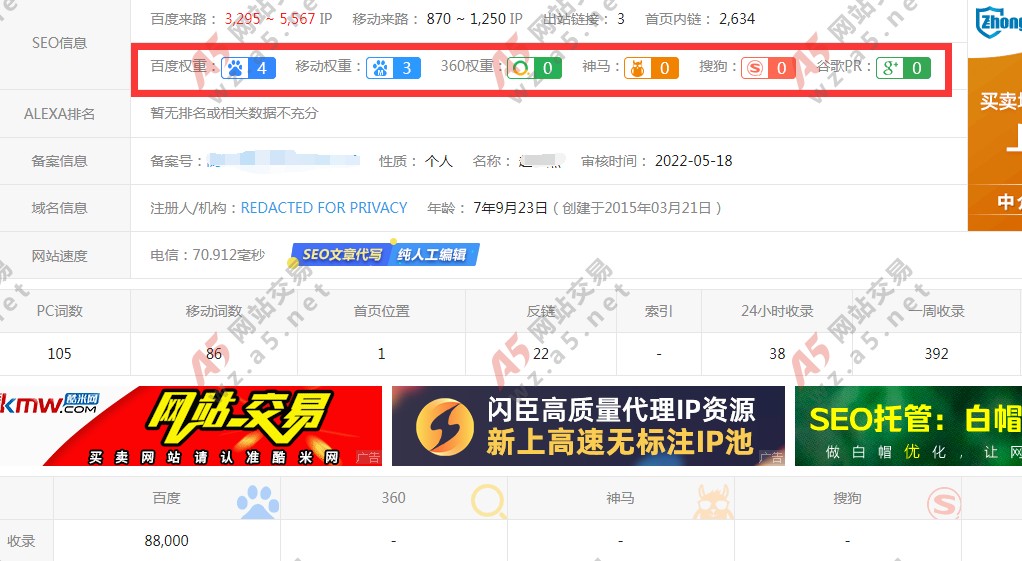
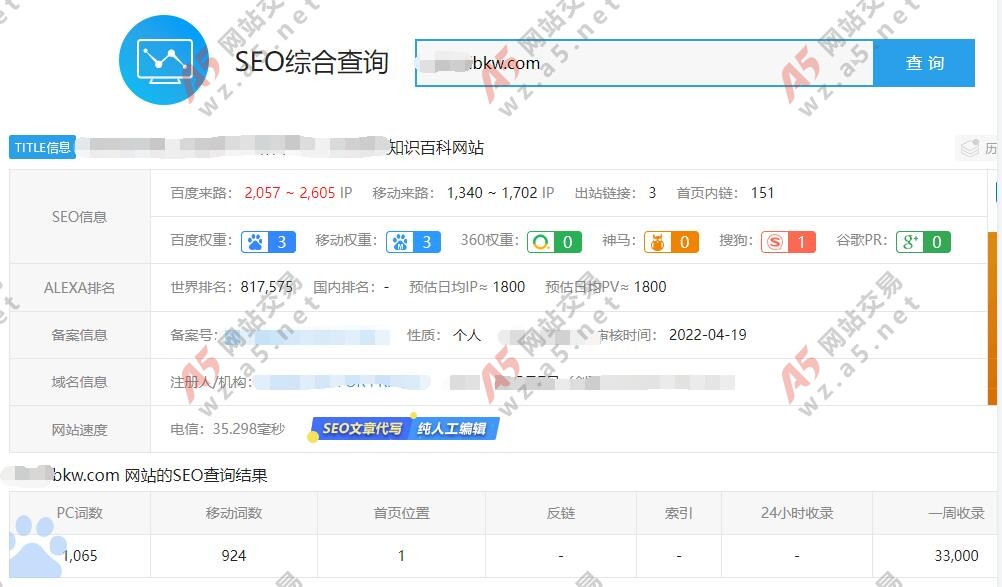
2024-01-15 17:06:03

最新YGBOOK小说程序,源码已经完美修复各类BUG,所有文件都已经解密完成,深度SEO源码,批量全自动后台采集,并且不需要很大的硬盘即可安装,易云采集了20W本小说占用不到20G,自带4条采集规则,源码压缩包有安装教程,跟着安装很简单的。 推荐安装的服务器跟源站是同一个地方的,例如源站是美国的,那可以选择美国服务器,这样采集的效量很高。
长文预警!!!
UWP 程序有 .NET Native 可以将程序集编译为本机代码,逆向的难度会大很多;而基于 .NET Framework 和 .NET Core 的程序却没有 .NET Native 的支持。虽然有 Ngen.exe 可以编译为本机代码,但那只是在用户计算机上编译完后放入了缓存中,而不是在开发者端编译。
于是有很多款混淆工具来帮助混淆基于 .NET 的程序集,使其稍微难以逆向。本文介绍 Smart Assembly 各项混淆参数的作用以及其实际对程序集的影响。
本文不会讲 SmartAssembly 的用法,因为你只需打开它就能明白其基本的使用。
感兴趣可以先下载:.NET Obfuscator, Error Reporting, DLL Merging - SmartAssembly。
准备
我们先需要准备程序集来进行混淆试验。这里,我使用 Whitman 来试验。它在 GitHub 上开源,并且有两个程序集可以试验它们之间的相互影响。
额外想吐槽一下,SmartAssembly 的公司 Red Gate 一定不喜欢这款软件,因为界面做成下面这样竟然还长期不更新:
而且,如果要成功编译,还得用上同为 Red Gate 家出品的 SQL Server,如果不装,软件到处弹窗报错。只是报告错误而已,干嘛还要开发者装一个那么重量级的 SQL Server 啊!详见:Why is SQL Server required — Redgate forums。
SmartAssembly
SmartAssembly 本质上是保护应用程序不被逆向或恶意篡改。目前我使用的版本是 6,它提供了对 .NET Framework 程序的多种保护方式:
- 强签名 Strong Name Signing
- 强签名可以确保程序之间的依赖关系是严格确定的,如果对其中的一个依赖进行篡改,将导致无法加载正确的程序集。
- 微软提供了强签名工具,所以可以无需使用 SmartAssembly 的:
- Sn.exe (Strong Name Tool) - Microsoft Docs
- How to: Sign an Assembly with a Strong Name - Microsoft Docs
- 自动错误上报 Automated Error Reporting
- SmartAssembly 会自动向 exe 程序注入异常捕获与上报的逻辑。
- 功能使用率上报 Feature Usage Reporting
- SmartAssembly 会修改每个方法,记录这些方法的调用次数并上报。
- 依赖合并 Dependencies Merging
- SmartAssembly 会将程序集中你勾选的的依赖与此程序集合并成一个整的程序集。
- 依赖嵌入 Dependencies Embedding
- SmartAssembly 会将依赖以加密并压缩的方式嵌入到程序集中,运行时进行解压缩与解密。
- 其实这只是方便了部署(一个 exe 就能发给别人),并不能真正保护程序集,因为实际运行时还是解压并解密出来了。
- 裁剪 Pruning
- SmartAssembly 会将没有用到的字段、属性、方法、事件等删除。它声称删除了这些就能让程序逆向后代码更难读懂。
- 名称混淆 Obfuscation
- 修改类型、字段、属性、方法等的名称。
- 流程混淆 Control Flow Obfuscation
- 修改方法内的执行逻辑,使其执行错综复杂。
- 动态代理 References Dynamic Proxy
- SmartAssembly 会将方法的调用转到动态代理上。
- 资源压缩加密 Resources Compression and Encryption
- SmartAssembly 会将资源以加密并压缩的方式嵌入到程序集中,运行时进行解压缩与解密。
- 字符串压缩加密 Strings Encoding
- SmartAssembly 会将字符串都进行加密,运行时自动对其进行解密。
- 防止 MSIL Disassembler 对其进行反编译 MSIL Disassembler Protection
- 在程序集中加一个 Attribute,这样 MSIL Disassembler 就不会反编译这个程序集。
- 密封类
- 如果 SmartAssembly 发现一个类可以被密封,就会把它密封,这样能获得一点点性能提升。
- 生成调试信息 Generate Debugging Information
- 可以生成混淆后的 pdb 文件
以上所有 SmartAssembly 对程序集的修改中,我标为 粗体 的是真的在做混淆,而标为 斜体 的是一些辅助功能。
后面我只会说明其混淆功能。
裁剪 Pruning
我故意在 Whitman.Core 中写了一个没有被用到的 internal 类 UnusedClass,如果我们开启了裁剪,那么这个类将消失。
▲ 没用到的类将消失
特别注意,如果标记了 InternalsVisibleTo,尤其注意不要不小心被误删了。
名称混淆 Obfuscation
类/方法名与字段名的混淆
名称混淆中,类名和方法名的混淆有三个不同级别:
- 等级 1 是使用 ASCII 字符集
- 等级 2 是使用不可见的 Unicode 字符集
- 等级 3 是使用高级重命名算法的不可见的 Unicode 字符集
需要注意:对于部分程序集, 类与方法名(NameMangling)的等级只能选为 3,否则混淆程序会无法完成编译 。
字段名的混淆有三个不同级别:
- 等级 1 是源码中字段名称和混淆后字段名称一一对应
- 等级 2 是在一个类中的不同字段使用不同名称即可(这不废话吗,不过 SmartAssembly 应该是为了强调与等级 1 和等级 3 的不同,必须写一个描述)
- 等级 3 是允许不同类中的字段使用相同的名字(这样能够更加让人难以理解)
需要注意:对于部分程序集, 字段名(FieldsNameMangling)的等级只能选为 2 或 3,否则混淆程序会无法完成编译 。
实际试验中,以上各种组合经常会出现无法编译的情况。
下面是 Whitman 中 RandomIdentifier 类中的部分字段在混淆后的效果:
// Token: 0x04000001 RID: 1 [CompilerGenerated] [DebuggerBrowsable(DebuggerBrowsableState.Never)] private int \u0001; // Token: 0x04000002 RID: 2 private readonly Random \u0001 = new Random(); // Token: 0x04000003 RID: 3 private static readonly Dictionary<int, int> \u0001 = new Dictionary<int, int>(); 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
这部分的原始代码可以在 冷算法:自动生成代码标识符(类名、方法名、变量名) 找到。
如果你需要在混淆时使用名称混淆,你只需要在以上两者的组合中找到一个能够编译通过的组合即可,不需要特别在意等级 1~3 的区别,因为实际上都做了混淆,1~3 的差异对逆向来说难度差异非常小的。
需要 特别小心如果有 InternalsVisibleTo 或者依据名称的反射调用,这种混淆下极有可能挂掉 !!! 请充分测试你的软件,切记 !!!
转移方法 ChangeMethodParent
如果开启了 ChangeMethodParent,那么混淆可能会将一个类中的方法转移到另一个类中,这使得逆向时对类型含义的解读更加匪夷所思。
排除特定的命名空间
如果你的程序集中确实存在需要被按照名称反射调用的类型,或者有 internal 的类/方法需要被友元程序集调用,请排除这些命名空间。
流程混淆 Control Flow Obfuscation
列举我在 Whitman.Core 中的方法:
public string Generate(bool pascal)
{
var builder = new StringBuilder();
var wordCount = WordCount <= 0 ? 4 - (int) Math.Sqrt(_random.Next(0, 9)) : WordCount;
for (var i = 0; i < wordCount; i++)
{
var syllableCount = 4 - (int) Math.Sqrt(_random.Next(0, 16));
syllableCount = SyllableMapping[syllableCount];
for (var j = 0; j < syllableCount; j++)
{
var consonant = Consonants[_random.Next(Consonants.Count)];
var vowel = Vowels[_random.Next(Vowels.Count)];
if ((pascal || i != 0) && j == 0)
{
consonant = CultureInfo.CurrentCulture.TextInfo.ToTitleCase(consonant);
}
builder.Append(consonant);
builder.Append(vowel);
}
}
return builder.ToString();
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
▲ 这个方法可以在 冷算法:自动生成代码标识符(类名、方法名、变量名) 找到。
流程混淆修改方法内部的实现。为了了解各种不同的流程混淆级别对代码的影响,我为每一个混淆级别都进行反编译查看。
▲ 没有混淆
0 级流程混淆
▲ 0 级流程混淆
1 级流程混淆
▲ 1 级流程混淆
可以发现 0 和 1 其实完全一样。又被 SmartAssembly 耍了。
2 级流程混淆
2 级流程混淆代码很长,所以我没有贴图:
// Token: 0x06000004 RID: 4 RVA: 0x00002070 File Offset: 0x00000270
public string Generate(bool pascal)
{
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
StringBuilder stringBuilder2;
if (-1 != 0)
{
stringBuilder2 = stringBuilder;
}
int num2;
int num = num2 = this.WordCount;
int num4;
int num3 = num4 = 0;
int num6;
int num8;
if (num3 == 0)
{
int num5 = (num <= num3) ? (4 - (int)Math.Sqrt((double)this._random.Next(0, 9))) : this.WordCount;
if (true)
{
num6 = num5;
}
int num7 = 0;
if (!false)
{
num8 = num7;
}
if (false)
{
goto IL_10E;
}
if (7 != 0)
{
goto IL_134;
}
goto IL_8E;
}
IL_6C:
int num9 = num2 - num4;
int num10;
if (!false)
{
num10 = num9;
}
int num11 = RandomIdentifier.SyllableMapping[num10];
if (6 != 0)
{
num10 = num11;
}
IL_86:
int num12 = 0;
int num13;
if (!false)
{
num13 = num12;
}
IL_8E:
goto IL_11E;
IL_10E:
string value;
stringBuilder2.Append(value);
num13++;
IL_11E:
string text;
bool flag;
if (!false)
{
if (num13 >= num10)
{
num8++;
goto IL_134;
}
text = RandomIdentifier.Consonants[this._random.Next(RandomIdentifier.Consonants.Count)];
value = RandomIdentifier.Vowels[this._random.Next(RandomIdentifier.Vowels.Count)];
flag = ((pascal || num8 != 0) && num13 == 0);
}
if (flag)
{
text = CultureInfo.CurrentCulture.TextInfo.ToTitleCase(text);
}
if (!false)
{
stringBuilder2.Append(text);
goto IL_10E;
}
goto IL_86;
IL_134:
if (num8 >= num6)
{
return stringBuilder2.ToString();
}
num2 = 4;
num4 = (int)Math.Sqrt((double)this._random.Next(0, 16));
goto IL_6C;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
▲ 2 级流程混淆
这时就发现代码的可读性降低了,需要耐心才能解读其含义。
3 级流程混淆
以下是 3 级流程混淆:
// Token: 0x06000004 RID: 4 RVA: 0x0000207C File Offset: 0x0000027C
public string Generate(bool pascal)
{
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
int num2;
int num = num2 = this.WordCount;
int num4;
int num3 = num4 = 0;
int num7;
int num8;
string result;
if (num3 == 0)
{
int num5;
if (num > num3)
{
num5 = this.WordCount;
}
else
{
int num6 = num5 = 4;
if (num6 != 0)
{
num5 = num6 - (int)Math.Sqrt((double)this._random.Next(0, 9));
}
}
num7 = num5;
num8 = 0;
if (false)
{
goto IL_104;
}
if (7 == 0)
{
goto IL_84;
}
if (!false)
{
goto IL_12A;
}
return result;
}
IL_73:
int num9 = num2 - num4;
num9 = RandomIdentifier.SyllableMapping[num9];
IL_81:
int num10 = 0;
IL_84:
goto IL_114;
IL_104:
string value;
stringBuilder.Append(value);
num10++;
IL_114:
string text;
bool flag;
if (!false)
{
if (num10 >= num9)
{
num8++;
goto IL_12A;
}
text = RandomIdentifier.Consonants[this._random.Next(RandomIdentifier.Consonants.Count)];
value = RandomIdentifier.Vowels[this._random.Next(RandomIdentifier.Vowels.Count)];
flag = ((pascal || num8 != 0) && num10 == 0);
}
if (flag)
{
text = CultureInfo.CurrentCulture.TextInfo.ToTitleCase(text);
}
if (!false)
{
stringBuilder.Append(text);
goto IL_104;
}
goto IL_81;
IL_12A:
if (num8 < num7)
{
num2 = 4;
num4 = (int)Math.Sqrt((double)this._random.Next(0, 16));
goto IL_73;
}
result = stringBuilder.ToString();
return result;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
▲ 3 级流程混淆
3 级流程混淆并没有比 2 级高多少,可读性差不多。不过需要注意的是,这些差异并不是随机差异,因为重复生成得到的流程结果是相同的。
4 级流程混淆
以下是 4 级流程混淆:
// Token: 0x06000004 RID: 4 RVA: 0x0000207C File Offset: 0x0000027C
public unsafe string Generate(bool pascal)
{
void* ptr = stackalloc byte[14];
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
StringBuilder stringBuilder2;
if (!false)
{
stringBuilder2 = stringBuilder;
}
int num = (this.WordCount <= 0) ? (4 - (int)Math.Sqrt((double)this._random.Next(0, 9))) : this.WordCount;
*(int*)ptr = 0;
for (;;)
{
((byte*)ptr)[13] = ((*(int*)ptr < num) ? 1 : 0);
if (*(sbyte*)((byte*)ptr + 13) == 0)
{
break;
}
*(int*)((byte*)ptr + 4) = 4 - (int)Math.Sqrt((double)this._random.Next(0, 16));
*(int*)((byte*)ptr + 4) = RandomIdentifier.SyllableMapping[*(int*)((byte*)ptr + 4)];
*(int*)((byte*)ptr + 8) = 0;
for (;;)
{
((byte*)ptr)[12] = ((*(int*)((byte*)ptr + 8) < *(int*)((byte*)ptr + 4)) ? 1 : 0);
if (*(sbyte*)((byte*)ptr + 12) == 0)
{
break;
}
string text = RandomIdentifier.Consonants[this._random.Next(RandomIdentifier.Consonants.Count)];
string value = RandomIdentifier.Vowels[this._random.Next(RandomIdentifier.Vowels.Count)];
bool flag = (pascal || *(int*)ptr != 0) && *(int*)((byte*)ptr + 8) == 0;
if (flag)
{
text = CultureInfo.CurrentCulture.TextInfo.ToTitleCase(text);
}
stringBuilder2.Append(text);
stringBuilder2.Append(value);
*(int*)((byte*)ptr + 8) = *(int*)((byte*)ptr + 8) + 1;
}
*(int*)ptr = *(int*)ptr + 1;
}
return stringBuilder2.ToString();
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
▲ 4 级流程混淆
我们发现,4 级已经开始使用没有含义的指针来转换我们的内部实现了。这时除了外部调用以外,代码基本已无法解读其含义了。
动态代理 References Dynamic Proxy
还是以上一节中我们 Generate 方法作为示例,在开启了动态代理之后(仅开启动态代理,其他都关掉),方法变成了下面这样:
// Token: 0x06000004 RID: 4 RVA: 0x0000206C File Offset: 0x0000026C
public string Generate(bool pascal)
{
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
int num = (this.WordCount <= 0) ? (4 - (int)\u0002.\u0002((double)\u0001.~\u0001(this._random, 0, 9))) : this.WordCount;
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++)
{
int num2 = 4 - (int)\u0002.\u0002((double)\u0001.~\u0001(this._random, 0, 16));
num2 = RandomIdentifier.SyllableMapping[num2];
for (int j = 0; j < num2; j++)
{
string text = RandomIdentifier.Consonants[\u0003.~\u0003(this._random, RandomIdentifier.Consonants.Count)];
string text2 = RandomIdentifier.Vowels[\u0003.~\u0003(this._random, RandomIdentifier.Vowels.Count)];
bool flag = (pascal || i != 0) && j == 0;
if (flag)
{
text = \u0006.~\u0006(\u0005.~\u0005(\u0004.\u0004()), text);
}
\u0007.~\u0007(stringBuilder, text);
\u0007.~\u0007(stringBuilder, text2);
}
}
return \u0008.~\u0008(stringBuilder);
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
▲ 动态代理
注意到 _random.Next(0, 9) 变成了 \u0001.~\u0001(this._random, 0, 9),Math.Sqrt(num) 变成了 \u0002.\u0002(num)。
也就是说,一些常规方法的调用被替换成了一个代理类的调用。那么代理类在哪里呢?
▲ 生成的代理类
生成的代理类都在根命名空间下。比如刚刚的 \u0001.~\u0001 调用,就是下面这个代理类:
// Token: 0x0200001A RID: 26
internal sealed class \u0001 : MulticastDelegate
{
// Token: 0x06000030 RID: 48
public extern \u0001(object, IntPtr);
// Token: 0x06000031 RID: 49
public extern int Invoke(object, int, int);
// Token: 0x06000032 RID: 50 RVA: 0x000030A8 File Offset: 0x000012A8
static \u0001()
{
MemberRefsProxy.CreateMemberRefsDelegates(25);
}
// Token: 0x04000016 RID: 22
internal static \u0001 \u0001;
// Token: 0x04000017 RID: 23
internal static \u0001 ~\u0001;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
字符串编码与加密 Strings Encoding
字符串统一收集编码 Encode
字符串编码将程序集中的字符串都统一收集起来,存为一个资源;然后提供一个辅助类统一获取这些字符串。
比如 Whitman.Core 中的字符串现在被统一收集了:
▲ 统一收集的字符串和解密辅助类
在我的项目中,统一收集的字符串可以形成下面这份字符串(也即是上图中 Resources 文件夹中的那个文件内容):
cQ==dw==cg==dA==eQ==cA==cw==ZA==Zg==Zw==aA==ag==aw==bA==eg==eA== Yw==dg==Yg==bg==bQ==dHI=ZHI=Y2g=d2g=c3Q=YQ==ZQ==aQ==bw==dQ==YXI= YXM=YWk=YWlyYXk=YWw=YWxsYXc=ZWU=ZWE=ZWFyZW0=ZXI=ZWw=ZXJlaXM=aXI= b3U=b3I=b28=b3c=dXI=MjAxOC0wOC0yNlQxODoxMDo0Mw==`VGhpcyBhc3NlbWJseSBoYXMgY mVlbiBidWlsdCB3aXRoIFNtYXJ0QXNzZW1ibHkgezB9LCB3aGljaCBoYXMgZXhwaXJlZC4=RXZhbHVh dGlvbiBWZXJzaW9uxVGhpcyBhc3NlbWJseSBoYXMgYmVlbiBidWlsdCB3aXRoIFNtYXJ0QXNzZW1ibHk gezB9LCBhbmQgdGhlcmVmb3JlIGNhbm5vdCBiZSBkaXN0cmlidXRlZC4=IA==Ni4xMi41Ljc5OQ== U21hcnRBc3NlbWJseQ==UGF0aA==U29mdHdhcmVcUmVkIEdhdGVc(U29mdHdhcmVcV293NjQzMk5vZ GVcUmVkIEdhdGVc 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
虽然字符串难以读懂,但其实我原本就是这么写的;给你看看我的原始代码就知道了(来自 冷算法:自动生成代码标识符(类名、方法名、变量名)):
private static readonly List<string> Consonants = new List<string>
{
"q","w","r","t","y","p","s","d","f","g","h","j","k","l","z","x","c","v","b","n","m",
"w","r","t","p","s","d","f","g","h","j","k","l","c","b","n","m",
"r","t","p","s","d","h","j","k","l","c","b","n","m",
"r","t","s","j","c","n","m",
"tr","dr","ch","wh","st",
"s","s"
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
生成的字符串获取辅助类就像下面这样不太容易读懂:
// Token: 0x0200000A RID: 10
public class Strings
{
// Token: 0x0600001C RID: 28 RVA: 0x00002B94 File Offset: 0x00000D94
public static string Get(int stringID)
{
stringID -= Strings.offset;
if (Strings.cacheStrings)
{
object obj = Strings.hashtableLock;
lock (obj)
{
string text;
Strings.hashtable.TryGetValue(stringID, out text);
if (text != null)
{
return text;
}
}
}
int index = stringID;
int num = (int)Strings.bytes[index++];
int num2;
if ((num & 128) == 0)
{
num2 = num;
if (num2 == 0)
{
return string.Empty;
}
}
else if ((num & 64) == 0)
{
num2 = ((num & 63) << 8) + (int)Strings.bytes[index++];
}
else
{
num2 = ((num & 31) << 24) + ((int)Strings.bytes[index++] << 16) + ((int)Strings.bytes[index++] << 8) + (int)Strings.bytes[index++];
}
string result;
try
{
byte[] array = Convert.FromBase64String(Encoding.UTF8.GetString(Strings.bytes, index, num2));
string text2 = string.Intern(Encoding.UTF8.GetString(array, 0, array.Length));
if (Strings.cacheStrings)
{
try
{
object obj = Strings.hashtableLock;
lock (obj)
{
Strings.hashtable.Add(stringID, text2);
}
}
catch
{
}
}
result = text2;
}
catch
{
result = null;
}
return result;
}
// Token: 0x0600001D RID: 29 RVA: 0x00002CF4 File Offset: 0x00000EF4
static Strings()
{
if (Strings.MustUseCache == "1")
{
Strings.cacheStrings = true;
Strings.hashtable = new Dictionary<int, string>();
}
Strings.offset = Convert.ToInt32(Strings.OffsetValue);
using (Stream manifestResourceStream = Assembly.GetExecutingAssembly().GetManifestResourceStream("{f6b5a51a-b2fb-4143-af01-e2295062799f}"))
{
int num = Convert.ToInt32(manifestResourceStream.Length);
Strings.bytes = new byte[num];
manifestResourceStream.Read(Strings.bytes, 0, num);
manifestResourceStream.Close();
}
}
// Token: 0x0400000C RID: 12
private static readonly string MustUseCache = "0";
// Token: 0x0400000D RID: 13
private static readonly string OffsetValue = "203";
// Token: 0x0400000E RID: 14
private static readonly byte[] bytes = null;
// Token: 0x0400000F RID: 15
private static readonly Dictionary<int, string> hashtable;
// Token: 0x04000010 RID: 16
private static readonly object hashtableLock = new object();
// Token: 0x04000011 RID: 17
private static readonly bool cacheStrings = false;
// Token: 0x04000012 RID: 18
private static readonly int offset = 0;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
生成字符串获取辅助类后,原本写着字符串的地方就会被替换为 Strings.Get(int) 方法的调用。
字符串压缩加密 Compress
前面那份统一收集的字符串依然还是明文存储为资源,但还可以进行压缩。这时,Resources 中的那份字符串资源现在是二进制文件(截取前 256 字节):
00000000: 7b7a 7d02 efbf bdef bfbd 4def bfbd efbf 00000010: bd7e 6416 efbf bd6a efbf bd22 efbf bd08 00000020: efbf bdef bfbd 4c42 7138 72ef bfbd efbf 00000030: bd54 1337 efbf bd0e 22ef bfbd 69ef bfbd 00000040: 613d efbf bd6e efbf bd35 efbf bd0a efbf 00000050: bd33 6043 efbf bd26 59ef bfbd 5471 efbf 00000060: bdef bfbd 2cef bfbd 18ef bfbd 6def bfbd 00000070: efbf bdef bfbd 64ef bfbd c9af efbf bdef 00000080: bfbd efbf bd4b efbf bdef bfbd 66ef bfbd 00000090: 1e70 efbf bdef bfbd ce91 71ef bfbd 1d5e 000000a0: 1863 efbf bd16 0473 25ef bfbd 2204 efbf 000000b0: bdef bfbd 11ef bfbd 4fef bfbd 265a 375f 000000c0: 7bef bfbd 19ef bfbd d5bd efbf bdef bfbd 000000d0: efbf bd70 71ef bfbd efbf bd05 c789 efbf 000000e0: bd51 eaae beef bfbd ee97 adef bfbd 0a33 000000f0: d986 141c 2bef bfbd efbf bdef bfbd 1fef 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
这份压缩的字符串在程序启动的时候会进行一次解压,随后就直接读取解压后的字符串了。所以会占用启动时间(虽然不长),但不会占用太多运行时时间。
为了能够解压出这些压缩的字符串,Strings 类相比于之前会在读取后进行一次解压缩(解密)。可以看下面我额外标注出的 Strings 类新增的一行。
using (Stream manifestResourceStream = Assembly.GetExecutingAssembly().GetManifestResourceStream("{4f639d09-ce0f-4092-b0c7-b56c205d48fd}"))
{
int num = Convert.ToInt32(manifestResourceStream.Length);
byte[] buffer = new byte[num];
manifestResourceStream.Read(buffer, 0, num);
++ Strings.bytes = SimpleZip.Unzip(buffer);
manifestResourceStream.Close();
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
至于嵌入其中的解压与解密类 SimpleZip,我就不能贴出来了,因为反编译出来有 3000+ 行:
字符串缓存 UseCache
与其他的缓存策略一样,每次获取字符串都太消耗计算资源的话,就可以拿内存空间进行缓存。
在实际混淆中,我发现无论我是否开启了字符串缓存,实际 Strings.Get 方法都会缓存字符串。你可以回到上面去重新阅读 Strings.Get 方法的代码,发现其本来就已带缓存。这可能是 SmartAssembly 的 Bug。
使用类的内部委托获取字符串 UseImprovedEncoding
之前的混淆都会在原来有字符串地方使用 Strings.Get 来获取字符串。而如果开启了这一选项,那么 Strings.Get 就不是全局调用的了,而是在类的内部调用一个委托字段。
比如从 Strings.Get 调用修改为 \u0010(),,而 \u0010 是我们自己的类 RandomIdentifier 内部的被额外加进去的一个字段 internal static GetString \u0010;。
防止 MSIL Disassembler 对其进行反编译 MSIL Disassembler Protection
这其实是个没啥用的选项,因为我们程序集只会多出一个全局的特性:
[assembly: SuppressIldasm] 1
只有 MSIL Disassembler 和基于 MSIL Disassembler 的工具认这个特性。真正想逆向程序集的,根本不会在乎 MSIL Disassembler 被禁掉。
dnSpy 和 dotPeek 实际上都忽略了这个特性,依然能毫无障碍地反编译。
dnSpy 可以做挺多事儿的,比如:
- 断点调试 Windows 源代码 - lindexi
- 神器如 dnSpy,无需源码也能修改 .NET 程序 - walterlv
密封
在 OtherOptimizations 选项中,有一项 SealClasses 可以将所有可以密封的类进行密封(当然,此操作不会修改 API)。
在上面的例子中,由于 RandomIdentifier 是公有类,可能被继承,所以只有预先写的内部的 UnusedClass 被其标记为密封了。
// Token: 0x02000003 RID: 3
internal sealed class UnusedClass
{
// Token: 0x06000007 RID: 7 RVA: 0x000026D0 File Offset: 0x000008D0
internal void Run()
{
}
// Token: 0x06000008 RID: 8 RVA: 0x000026D4 File Offset: 0x000008D4
internal async Task RunAsync()
{
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
实际项目中,我该如何选择
既然你希望选择“混淆”,那么你肯定是希望能进行最大程度的保护。在保证你没有额外产生 Bug,性能没有明显损失的情况下,能混淆得多厉害就混淆得多厉害。
基于这一原则,我推荐的混淆方案有(按推荐顺序排序):
- 流程混淆
- 建议必选
- 直接选用 4 级流程(不安全代码)混淆,如果出问题才换为 3 级(goto)混淆,理论上不需要使用更低级别
- 流程混淆对性能的影响是非常小的,因为多执行的代码都是有编译期级别优化的,没有太多性能开销的代码
- 流程混淆仅影响实现,不修改 API,所以基本不会影响其他程序各种对此程序集的调用
- 名称混淆
- 尽量选择
- 任意选择类/方法名和字段名的级别,只要能编译通过就行(因为无论选哪个,对程序的影响都一样,逆向的难度差异也较小)
- 名称混淆不影响程序执行性能,所以只要能打开,就尽量打开
- 如果有 InternalsVisibleTo 或者可能被其他程序集按名称反射调用,请:
- 关闭此混淆
- 使用 Exclude 排除特定命名空间,使此命名空间下的类/方法名不进行名称混淆
- 如果你能接受用 Attribute 标记某些类不应该混淆类名,也可以使用这些标记(只是我不推荐这么做,这让混淆污染了自己的代码)
- 动态代理
- 推荐选择
- 动态代理仅影响实现,不修改 API,所以基本不会影响其他程序各种对此程序集的调用
- 动态代理会生成新的类/委托来替换之前的方法调用,所以可能造成非常轻微的性能损失(一般可以忽略)
- 字符串压缩加密
- 可以选择
- 由于所有的字符串都被统一成一个资源,如果额外进行压缩加密,那么逆向时理解程序的含义将变得非常困难(没有可以参考的锚点)
- 会对启动时间有轻微的性能影响,如果额外压缩加密,那么会有更多性能影响;如果你对启动性能要求较高,还是不要选了
- 会轻微增加内存占用和读取字符串时的 CPU 占用,如果你对程序性能要求非常高,还是不要选了
以上四种混淆方式从四个不同的维度对你类与方法的实现进行了混淆,使得你写的类的任何地方都变得无法辨认。流程混淆修改方法内实现的逻辑,名称混淆修改类/属性/方法的名称,动态代理将方法内对其他方法的调用变得不再直接,字符串压缩加密将使得字符串不再具有可读的含义。对逆向阅读影响最大的就是以上 4 种混淆了,如果可能,建议都选择开启。
如果你的程序中有需要保护的“嵌入的资源”,在没有自己的保护手段的情况下,可以使用“资源压缩加密”。不过,我更加推荐你自己进行加密。
至于 SmartAssembly 推荐的其他选项,都是噱头重于实际效果:
- 裁剪
- 一般也不会有多少开发者会故意往程序集中写一些不会用到的类吧!
- 依赖合并/依赖嵌入
- 并不会对逆向造成障碍,开不开启差别不大,反而降低了性能
- 防止 MSIL Disassembler 反编译
- 并不会对逆向造成障碍,防君子不防小人
- 密封类
- 声称可以提升性能,但这点性能提升微乎其微
SmartAssembly 的官方文档写得还是太简单了,很难得到每一个设置项的含义和实际效果。
以上这些信息的得出,离不开 dnSpy 的反编译。